Introduction to Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
The term microeconomics and macroeconomics were coined by Ragnar Frisch in 1930. He classified economics into two branches; Microeconomics and macroeconomics. These terms derived from the Greek word, Mikro and makro, which means small and large respectively. Microeconomics studies the economic behavior of individual decision-making units i.e. individual household, worker, firm, or industry, and price determination of individual goods and services. In contrast, macroeconomics is concerned with the behavior of aggregate, the economy as a whole. In other words, we can define macroeconomics as concerned with the nature, relationships, and behavior of such economic aggregates as national income, total consumption, saving and investment, total employment, and the general price level.
What is the difference between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics?
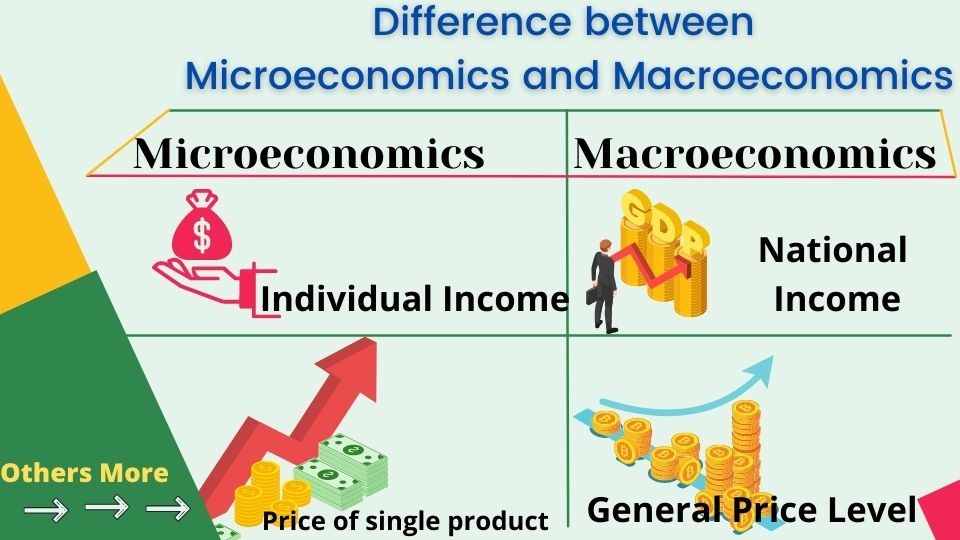
The main difference between microeconomics and macroeconomics is; Microeconomics studies the activity of small economic units like individual income, consumer, producer, firm, etc but Macroeconomics studies the activity of the economy as a whole, like national income, national consumption, total expenditure, etc.
Other differences between microeconomics and macroeconomics are:
Nature of Study
Microeconomics studies the activity of individual units such as individual income, individual expenditure, individual consumption, etc. On the other hand, Macroeconomics studies the activities of an aggregate of microeconomics variables, not the individual income but the National income, not the individual expenditure but national expenditure, not the individual consumption but the national consumption, etc.
Basic Assumption
Microeconomics assumes all the macro variables constant i.e. there is a constant level of national income, consumption, expenditure, price level, etc whereas Macroeconomics assumes all the microeconomics variables constant. It assumes economic decisions of households and firms, price of individual products, etc are constant or given
Objectives
The major objectives of microeconomics are for optimization and maximization of personal gains and profits. Maximization of consumer’s utility under budget constraint and maximization of producer’s profit or minimization of loss under the least-cost input choice Whereas the major objectives of macroeconomics are for Long-term growth, maintenance of high levels of production, and employment on the economy as a whole.
Subject Matters
Microeconomics deals with the process of pricing with the demand and supply forces of the market so it also called price theory. On the other hand, Macroeconomics deals with the process of income and employment determination. So, it also called income and employment theory.
Methodology
Microeconomics is based on partial equilibrium analysis i.e. analysis of each unit/variable of microeconomics keeping others constants but Macroeconomics is based on general equilibrium analysis i.e. analysis of all economic variables simultaneously.
Components of equilibrium
In microeconomics, the equilibrium of the market is determined by the demand and supply forces of the market but In macroeconomics, the equilibrium of the market is determined by aggregate demand and aggregate supply forces of the market.
Types of analysis
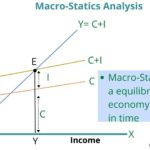
Microeconomics studies the equilibrium at a point in time. It ignores the time lag whereas Macroeconomics is based on time lag, rate of change, past and expected value of variables. Its studies are based on dynamic analysis. (For more)
Solution of problems
The study of microeconomics is not of much help to solve the important current issues and problems such as the decline in national income, hyperinflation, widespread unemployment, and so on Whereas macroeconomics studies the causes, effects, and possible measures for the solution of these issues and problems.
Difference between microeconomics and macroeconomics in tabular form
| Basis | Microeconomics | Macroeconomics |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Microeconomics studies the activity of small economic units like individual income, consumer, producer, firm, etc | Macroeconomics studies the activity of the economy as a whole, like national income, national consumption, total expenditure, etc. |
| Assumption | Microeconomics assumes all the macro variables constant i.e. there is a constant level of national income, consumption, expenditure, price level, etc | Macroeconomics assumes all the microeconomics variables constant. It assumes economic decisions of households and firms, price of individual products, etc are constant or given. |
| Objectives | Optimization and maximization of personal gains and profits. Maximization of consumer’s utility under budget constraint and also maximization of producer’s profit or minimization of loss under the least-cost input choice | Long-term growth, maintenance of high levels of production, and also employment on the economy as a whole. |
| Subject matter | Microeconomics deals with the process of pricing with the demand and supply forces of the market. So it is also called price theory. | Macroeconomics deals with the process of income and employment determination. so it is also called income and employment theory. |
| Methodology | Microeconomics is based on partial equilibrium analysis i.e. analysis of each unit/variable of microeconomics keeping others constants. | Macroeconomics is based on general equilibrium analysis i.e. analysis of all economic variables simultaneously. |
| Components of equilibrium | In microeconomics, the equilibrium of the market is determined by the demand and supply forces of the market. | In macroeconomics, the equilibrium of the market is determined by aggregate demand and aggregate supply forces of the market. |
| Types of analysis | Microeconomics studies the equilibrium at a point in time. It ignores the time lag. | Macroeconomics is based on time lag, rate of change, past and expected value of variables. Its studies are based on dynamic analysis. |
| Solution of problems | The study of microeconomics is not of much help to solve the important current issues and problems such as the decline in national income, hyperinflation, widespread unemployment, and so on. | Macroeconomics studies the causes, effects, and possible measures for the solution of current issues and problems such as the decline in national income, hyperinflation, widespread unemployment, and so on. |
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is macroeconomics is known as income and employment theory?
Macroeconomics also known as income and employment theory because it studies the process of income and employment determination, and also factors determining income and employment
Why microeconomics is known as price theory?
Microeconomics is known as price theory because it deals with the process of pricing with the demand and supply forces of the market.